Varicose veins and Arterial disease
Vascular care involves the diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions affecting the blood vessels—arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels. Vascular care is typically provided by vascular specialists or vascular surgeons and may include both medical and surgical interventions. Here are key aspects of vascular care:
Common Vascular Conditions:
⦁ Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
- Narrowing or blockage of arteries, usually in the legs, which can lead to reduced blood flow.
⦁ Aneurysms:
- Abnormal bulges or weakened areas in blood vessel walls, which can be life-threatening if they rupture.
⦁ Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
- Formation of blood clots in deep veins, often in the legs, which can lead to serious complications.
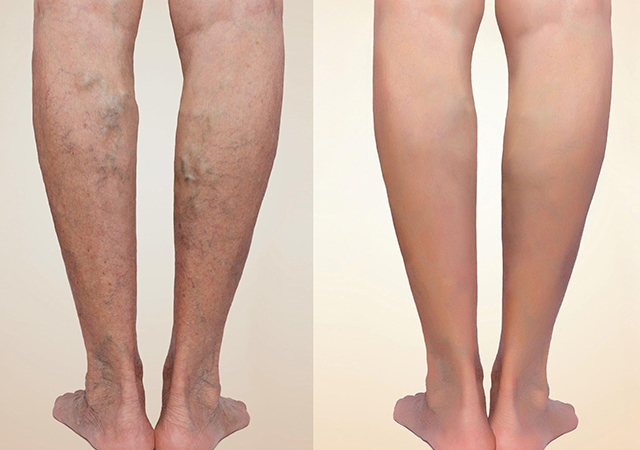
⦁ Varicose Veins:
- Enlarged and twisted veins, usually in the legs, caused by faulty valves that allow blood to pool.
⦁ Carotid Artery Disease:
- Narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
⦁ Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI):
- Impaired blood flow in the veins, leading to symptoms like leg swelling and skin changes.
⦁ Lymphedema:
- Swelling caused by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, often associated with lymph node removal or damage.
⦁ Renal Artery Disease:
- Narrowing or blockage of the arteries supplying blood to the kidneys, which can lead to high blood pressure and kidney problems
Diagnostic Tools:
⦁ Vascular Imaging:
- Non-invasive imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs to visualize blood vessels and diagnose conditions.
⦁ Angiography:
- A procedure that uses contrast dye and X-rays to examine the blood vessels, often performed for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
Medical Management:
⦁ Medications:
- Prescription medications may be used to manage conditions such as blood clots, hypertension, and cholesterol.
⦁ Lifestyle Modifications:
- Recommendations for lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, to improve vascular health.
Interventional Procedures:
⦁ Angioplasty and Stenting:
- Inflating a balloon to open narrowed or blocked arteries, often followed by the placement of a stent to keep the vessel open.
⦁ Atherectomy:
- Removing plaque buildup from arteries using specialized tools.
⦁ Thrombectomy:
- Surgical removal of blood clots, often performed in cases of deep vein thrombosis.
⦁ Vein Ablation:
- Using heat or laser energy to close off varicose veins.
⦁ Endarterectomy:
- Surgical removal of plaque from the lining of an artery, often performed in the carotid arteries.
Surgical Interventions:
⦁ Bypass Surgery:
- Creating a graft to redirect blood flow around a blocked or narrowed artery.
⦁ Aneurysm Repair:
- Surgical repair or endovascular stent graft placement to treat aneurysms.
⦁ Vascular Access Surgery:
- Creating access points for dialysis or other medical treatments requiring access to blood vessels.
Follow-Up and Monitoring:
⦁ Postoperative Care:
- Monitoring and managing patients after vascular procedures or surgeries.
⦁ Long-Term Surveillance:
- Regular follow-up to monitor the progression of vascular conditions and assess the effectiveness of treatments
Collaborative Care:
⦁ Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as cardiologists, nephrologists, and radiologists, for comprehensive care.
