What are Pacemaker and Defibrillator?
What are Pacemaker and Defibrillator? Pacemakers and Defibrillators are devices that help control the heart rhythms in case of irregular heartbeats through electrical shocks. They monitor the patient’s heart and regulate possible life-threatening abnormal heartbeats.
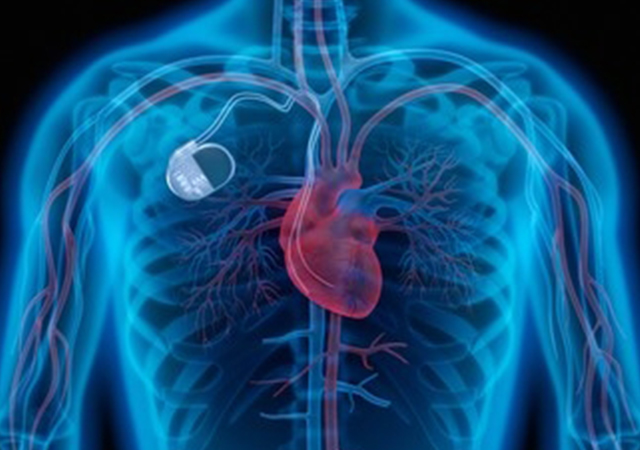
A pacemaker is a small device implanted in the chest using a surgical process. It sends electrical impulses to prevent the heart from beating too slow. However, it only functions when needed, such as sending electrical signals during bradycardia (slow heartbeat).
A pacemaker has a pulse generator that controls the rate of electrical impulses and electrodes that connect to the heart chambers to pass the electric signals.
A defibrillator, also known as implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), is an electronic device connected to the heart to detect rapid or abnormal heartbeat and send electrical shocks to bring the pace back to normal.
Why are Pacemaker and Defibrillator used?
An internal pacemaker is generally implanted below the collar bone. It is seen as necessary when:
- You have a slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
- After a heart attack and to treat possible heart failure
- To correct the heart rhythms after surgery or medication
An implantable defibrillator is placed in patients who are at risk of life-threatening rapid heart rhythm. ICD is necessary to those patients who have survived cardiac arrests. In addition:
- It corrects ventricular tachycardia
- It prevents heart failure
- Acts as a precaution for people with inherited heart conditions or problems with heart contraction
What are the risks of Pacemaker and Defibrillator?
Risks and complications while implanting a pacemaker or a defibrillator are uncommon, but they can happen. The patient must inform the physician if they are pregnant, breastfeeding, allergic to any medicines, or has any medical condition to reduce the possible risks.
Some of the risks related to pacemaker surgery are:
- Infection, swelling, bruising, or bleeding at the site of the pacemaker
- Blood clots or damage to blood vessels near the pacemaker
- Collapsed lung
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Bleeding or damage to the blood vessel at the catheter insertion site
- Injury to heart or collapsed lung
- Wound infection
- Unexpected dangerous heart arrhythmia
What are the preparations necessary for a Pacemaker and Defibrillator?
Prior to a pacemaker or defibrillator surgery, the patient must inform the physician if they are allergic to any medicines or latex or if they are pregnant. Also, the patient must inform the physician about any prescription they are taking and about any heart condition. Fasting for a certain period will also be recommended. The physicians will inform you of other instructions prior to the procedure.
Before getting a pacemaker, you must go through several tests to diagnose the irregular heartbeat. Some tests include ECG (electrocardiogram), echocardiogram, stress test, holter monitoring, etc.
After the procedure, you must refrain from vigorous exercise and heavy lifting. You will also need to take precautions while near cellphones, metal detectors, power generating equipment, and more.
